RBF Morph Fluids is an add-on that enables shape optimization studies entirely within ANSYS Fluent by morphing an existing mesh
Optimize shapes by morphing existing, trusted meshes
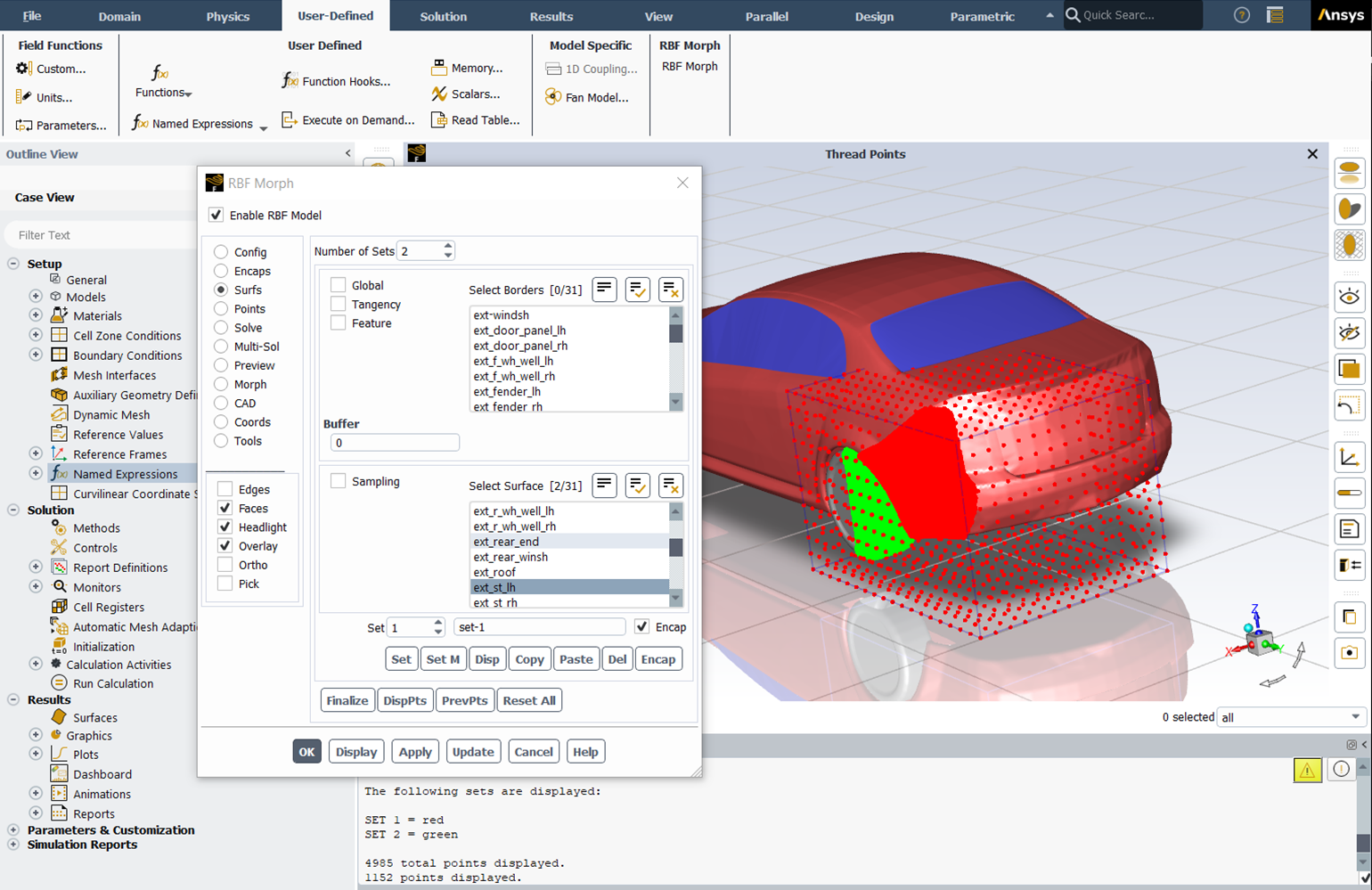
This new approach leverages ANSYS Fluent’s advanced CFD technology and overcomes the limitations of conventional methods by introducing new functionalities through dedicated routines implemented directly within the ANSYS Fluent code.
A dedicated Graphical User Interface (GUI) has been developed and fully integrated into ANSYS Fluent. The product supports CFD users without requiring them to learn a new software package.
Key features include:
- Product Integration: full integration within ANSYS Fluent.
- User Interface: dedicated GUI and TUI (scriptable).
- Process Integration: morphing directly inside the solving stage without modifying the geometry, regenerating the mesh and setup again the case.
- Mesh Topology: modification of the original surface and volume mesh producing a nodal smoothing without changing the mesh topology.
- Surface Morphing: surface meshes can be modified by free surface deformation, rigid movement or scaling.
- Volume Smoothing: high quality smoothing of the volume mesh with relatively large movements possible in a single step deformation.
- Versatility: nodal smoothing is achieved by means of a meshless approach that is independent from the mesh structure, handling every kind of mesh element type (tetrahedral, hexahedral, polyhedral, prismatic, hexcore, non-conformal interfaces, etc.).
- Reusability: the RBF solution can be applied to any mesh representing the same geometry.
- Consistency: mesh characteristics are preserved so mesh consistency is ensured (element size, type and distribution, prism layers, etc.).
- Parallelism: parallel calculation for large models (many millions of cells).
- Efficiency: flow solutions are fully readable through all the morphed mesh, reducing the number of iterations to converge.
- Precision: exact movement is ensured for the moving nodes locations as well as exact feature preservation.
- Parameterization: multi-parameter and multi-step problems.
- CAD: transfer modifications back to CAD by applying to STEP files similar modifications done on the mesh in order to fully support the re-design of the morphed surfaces.
- Automatic shape sculpting driven by CFD solution results (Adjoint Solver).
- Product Integration: full integration with ANSYS Fluent.
- User Interface: dedicated GUI and TUI (scriptable).
- Process Integration: morphing directly inside the solving stage without modifying the geometry, regenerating the mesh and setup again the case.
- Mesh Topology: modification of the original surface and volume mesh producing a nodal smoothing without changing the mesh topology.
- Surface Morphing: surface meshes can be modified by free surface deformation, rigid movement or scaling.
- Volume Smoothing: high quality smoothing of the volume mesh with relatively large movements possible in a single step deformation.
- Versatility: nodal smoothing is achieved by means of a meshless approach that is independent from the mesh structure, handling every kind of mesh element type (tetrahedral, hexahedral, polyhedral, prismatic, hexcore, non-conformal interfaces, etc.).
- Reusability: the RBF solution can be applied to any mesh representing the same geometry.
- Consistency: mesh characteristics are preserved so mesh consistency is ensured (element size, type and distribution, prism layers, etc.).
- Parallelism: parallel calculation for large models (many millions of cells).
- Efficiency: flow solutions are fully readable through all the morphed mesh, reducing the number of iterations to converge.
- Precision: exact movement is ensured for the moving nodes locations as well as exact feature preservation.
- Parameterization: multi-parameter and multi-step problems.
- CAD: transfer modifications back to CAD by applying to STEP files similar modifications done on the mesh in order to fully support the re-design of the morphed surfaces.
- Automatic shape sculpting driven by CFD solution results (Adjoint Solver).


